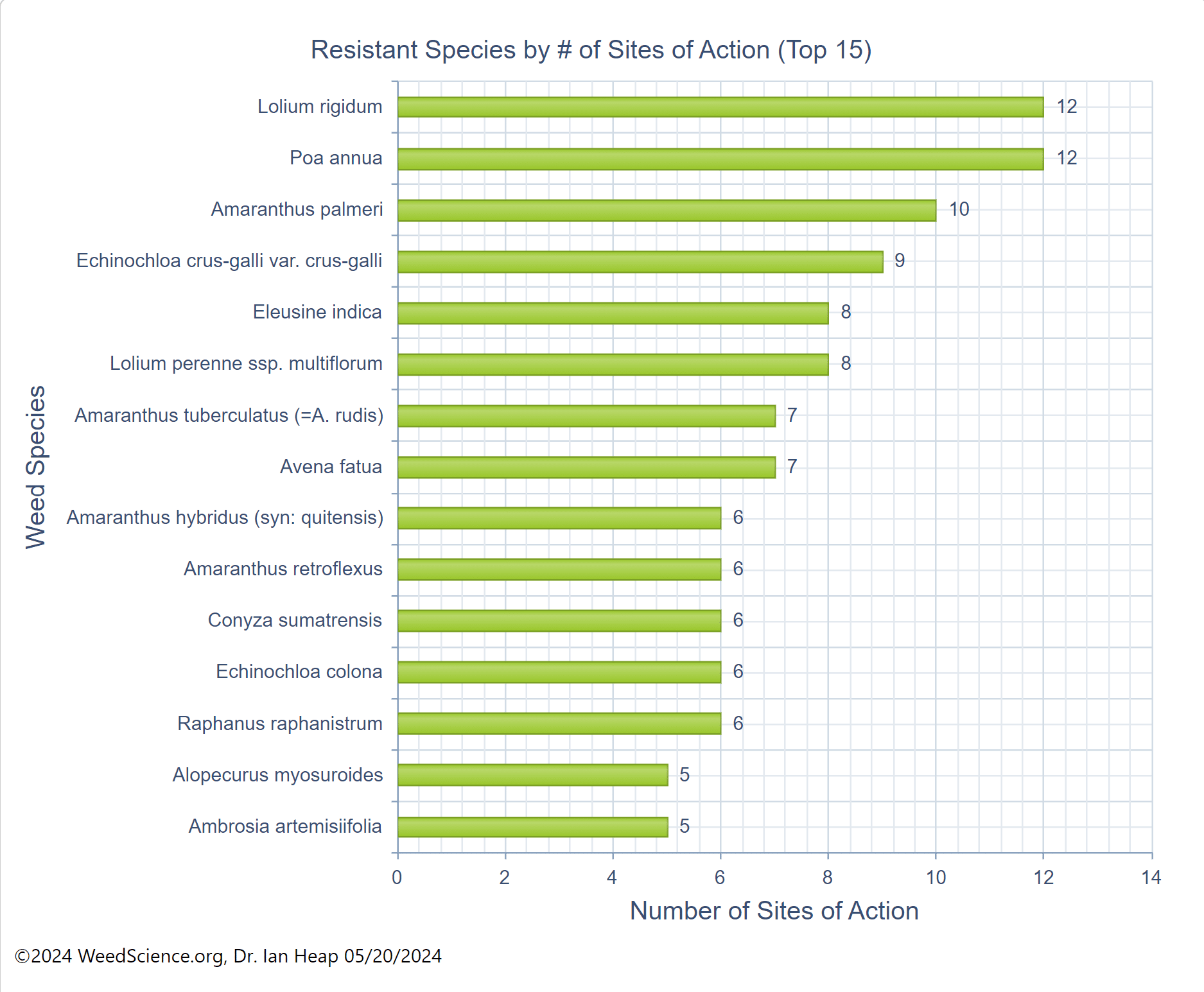
Combatting herbicide resistance relies on understanding herbicide Sites of Action (SOA). The Take Action Herbicide Classification Chart helps farmers, crop consultants, and the ag-retailer industry to understand Site of Action across many commonly used herbicides and improve herbicide rotation. Herbicide rotation in combination with other integrated weed management strategies is critical to help prolong the utility of herbicides.
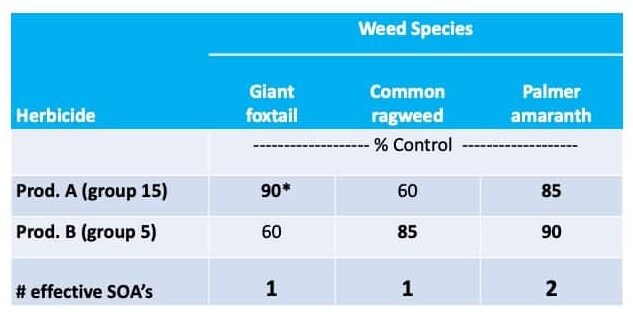
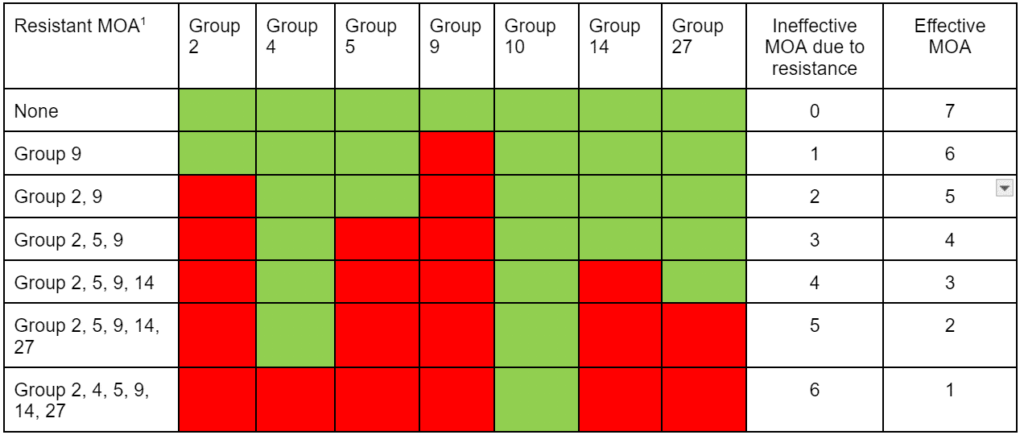
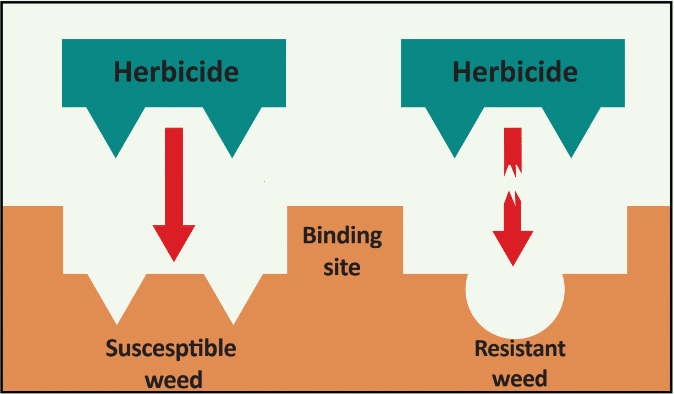
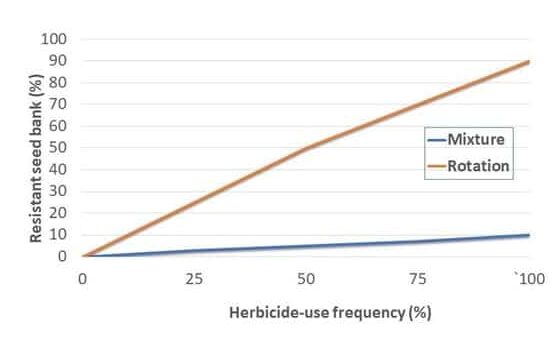
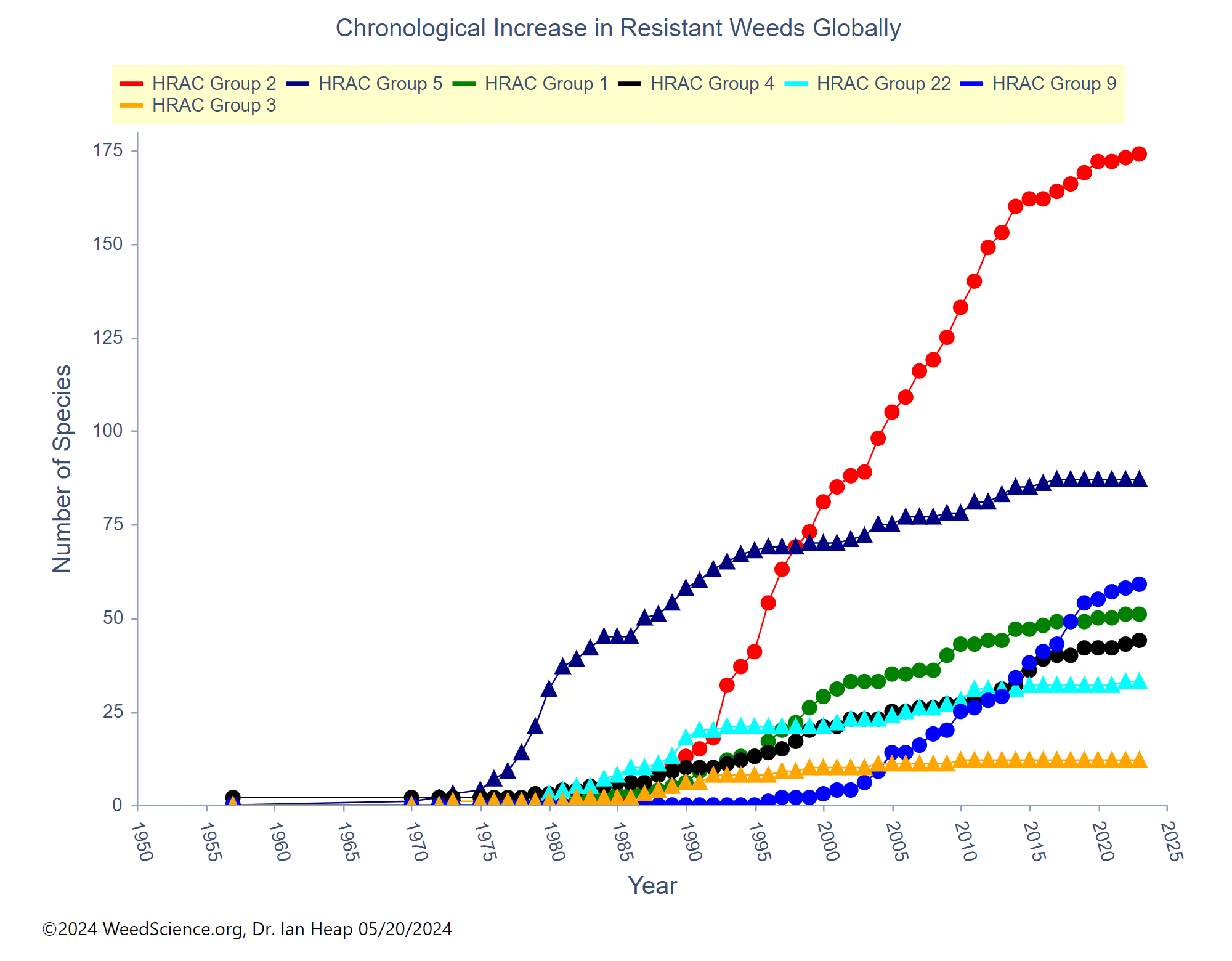
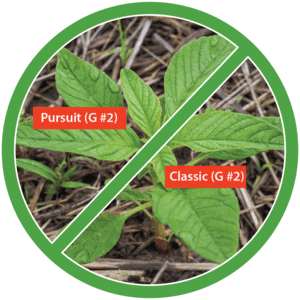
One of the major causes of weed resistance is the overuse of the same herbicide (or similar herbicides with the same SOA) without sufficient herbicide rotation. One of the Best Management Practices (BMP) to avoid herbicide resistance is using herbicides with different sites of action as a tank-mixture or as sequential treatments. As a result, if a weed is resistant to a specific herbicide SOA it is effectively controlled by other herbicides with a different SOA. In order for this strategy to be effective, herbicides used in combination must belong to different sites of action AND be effective on the weed species.
Is herbicide Mode of Action the same as Site of Action? NO.
Mode of Action is the plant processes affected by the herbicide, or the entire sequence of events that results in death of susceptible plants. Herbicides from very different chemical families may have the same mechanism of action.
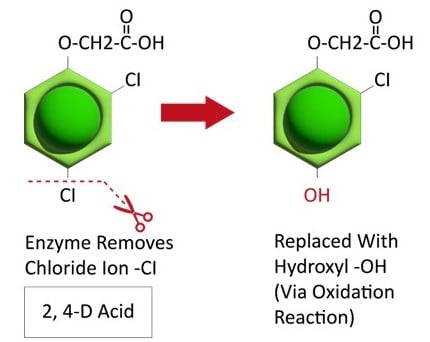
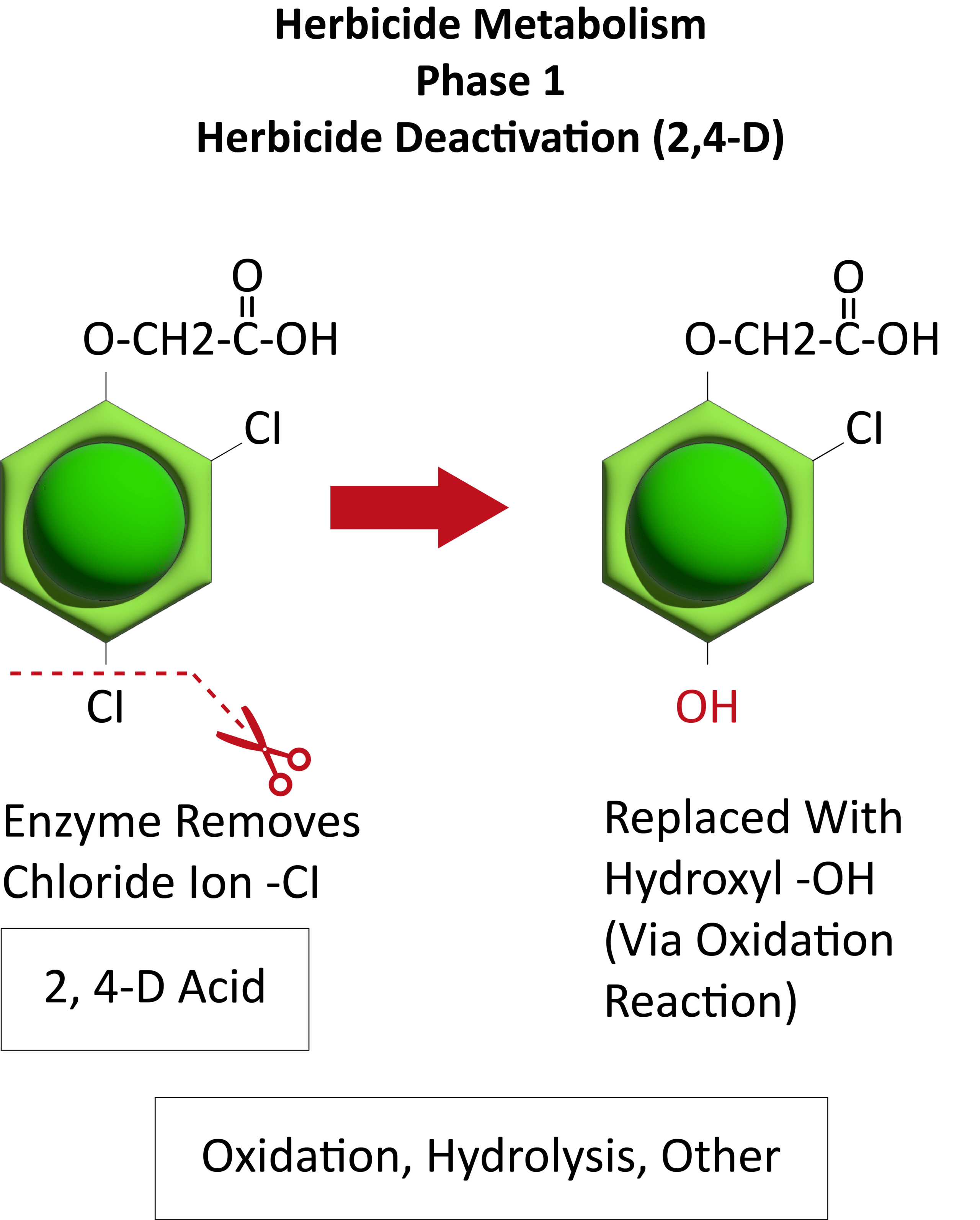
Site of Action is the biochemical site within a plant where the herbicide directly interacts. SOA is sometimes called mechanism of action. This is often at an enzyme within a plant cell. There are many more sites of action than there are modes of action. Currently there are over 20 sites of action. The numbers listed on herbicide labels and containers correspond to the sites of action.
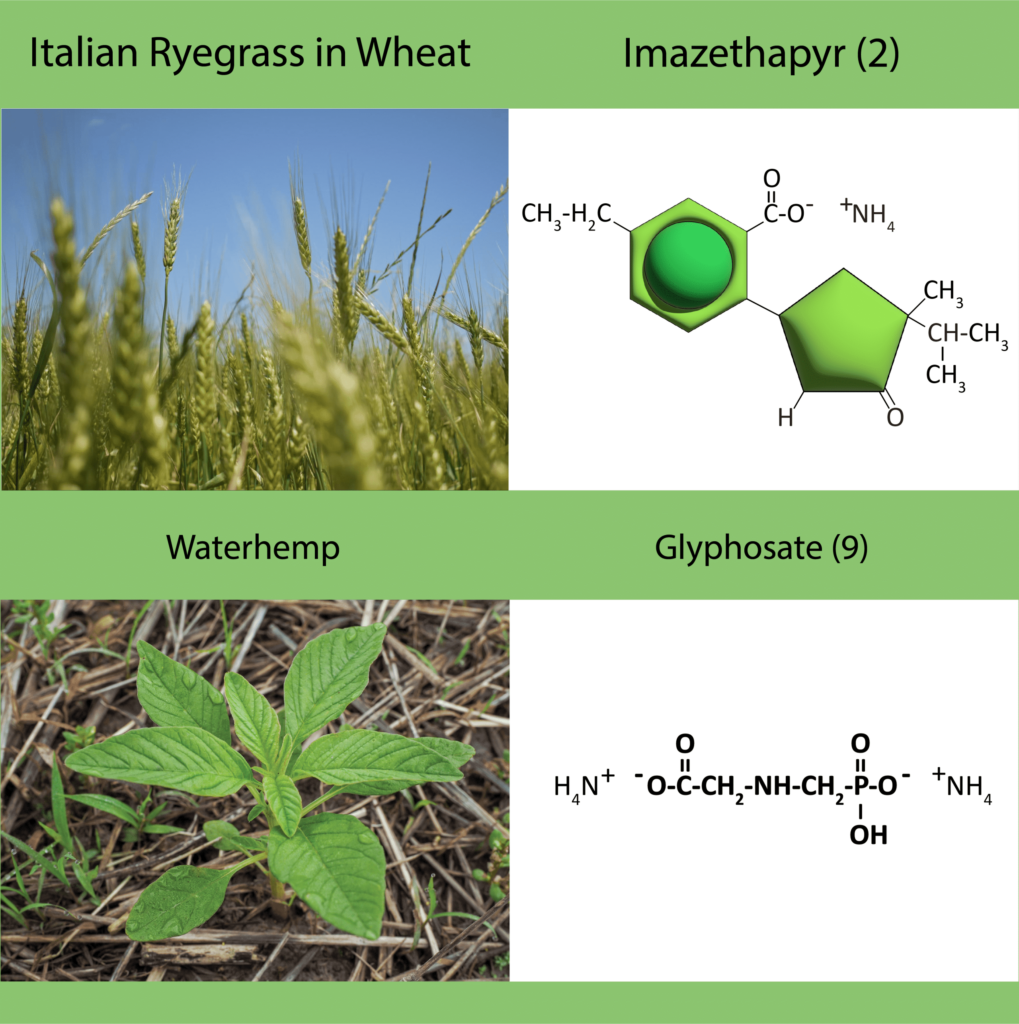
“Effective” Site of Action describes the situation when using a SOA and it is effective at controlling the weed. For instance, tanking mixing two herbicides with different SOA, but only one of the herbicides will kill the weed, there is only one effective SOA. Similarly, if you have glyphosate-resistant Palmer amaranth in your field, tank-mixing dicamba (active ingredient in Xtendimax™ or Engenia™ herbicide, WSSA group 4) and glyphosate (Roundup, WSSA group 9) only provides one effective mode of action. So using dicamba plus glyphosate alone is exerting high selection pressure for resistance to dicamba. It is therefore important to be aware of weed resistance in your field and region, and develop a strong management program containing multiple effective herbicide sites of action.
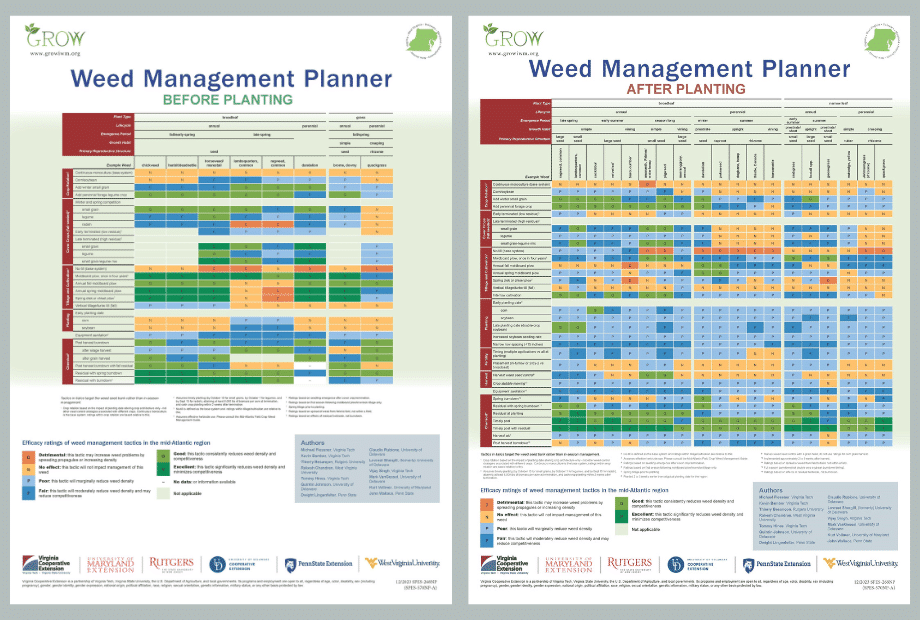
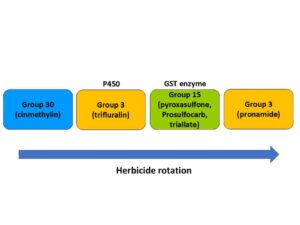
How to use the Herbicide Classification Chart: The Herbicide Classification Chart is an important resource for managing herbicide resistance. By knowing herbicide groups by their site of action (SOA) and herbicide effectiveness**, diversified herbicide programs can be developed.
The left half of the chart classifies herbicides first by their mode of action (MOA) and then further classifies them by site of action (SOA). For example, Herbicide Groups 2 and 9 are both Amino Acid Synthesis Inhibitors, which means their MOA is to shut down amino acids necessary for protein synthesis and ultimately plant growth. However, Groups 2 and 9 have different SOA. Group 2 herbicides inhibit the enzyme acetolactate synthase (ALS), while Group 9 herbicide (glyphosate) inhibits the enzyme enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate synthase (EPSPS).
The right half of the chart lists herbicide premixes and includes their individual herbicides and sites of action (SOA). Premixes on this chart are some of the more common brand names. If you use a different brand, you will need to look on the label for the active ingredients.
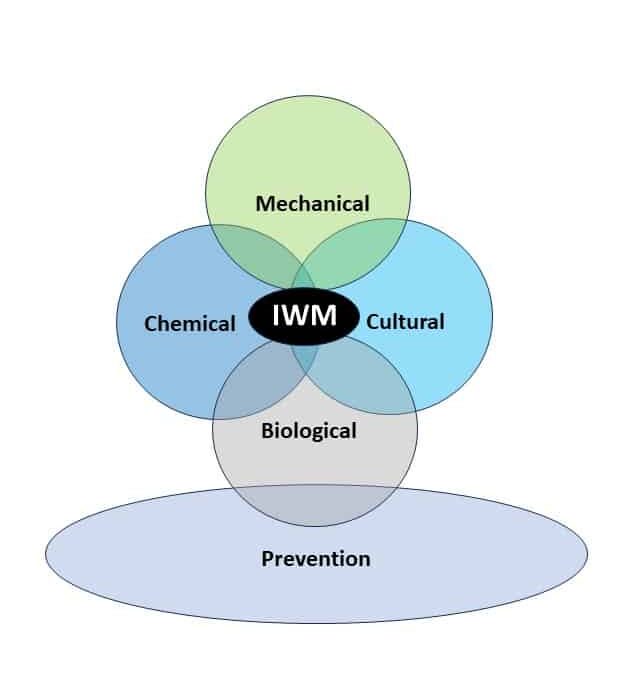
In addition to using herbicides with effective, multiple sites of action be sure to include effective non-chemical strategies for weed control.
**Refer to your local university herbicide recommendation book for information on herbicide effectiveness.
Resources:
Article by Mark VanGessel, University of Delaware and Claudio Rubione, GROW